Interactive Control Systems Tools
Bode Diagram
A Bode diagram consists of two graphs: one is a plot of the logarithm of the magnitude of a sinusoidal transfer function; the other is a plot of the phase angle. Both are plotted against the frequency (in degrees) in logarithmic scale.
The standard representation of the logarithmic magnitude is
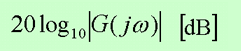
where the base of the logarithm is 10. The unit used in this representation is the decibel, usually abbreviated dB. In the logarithmic representation, the curves are drawn on semilog paper, using the log scale for frequency and the linear scale for either magnitude (but in decibels) or phase angle (in degrees).
The representation of the phase angle is usually denoted as

The main advantage of using the Bode diagram is that multiplication of magnitudes can be converted into addition. Furthermore, a simple method for sketching an approximate log-magnitude curve is available. It is based on asymptotic approximations. However, it is easy to plot the exact curves by adding the necessary corrections to the basic asymptotic ones.
(See also the Basic Definitions about Bode Diagram)